Python Linked List: Create a doubly linked list, append some items and iterate through the list
Python Linked List: Exercise-8 with Solution
Write a Python program to create a doubly linked list, append some items and iterate through the list (print forward).
Sample Solution:-
Python Code:
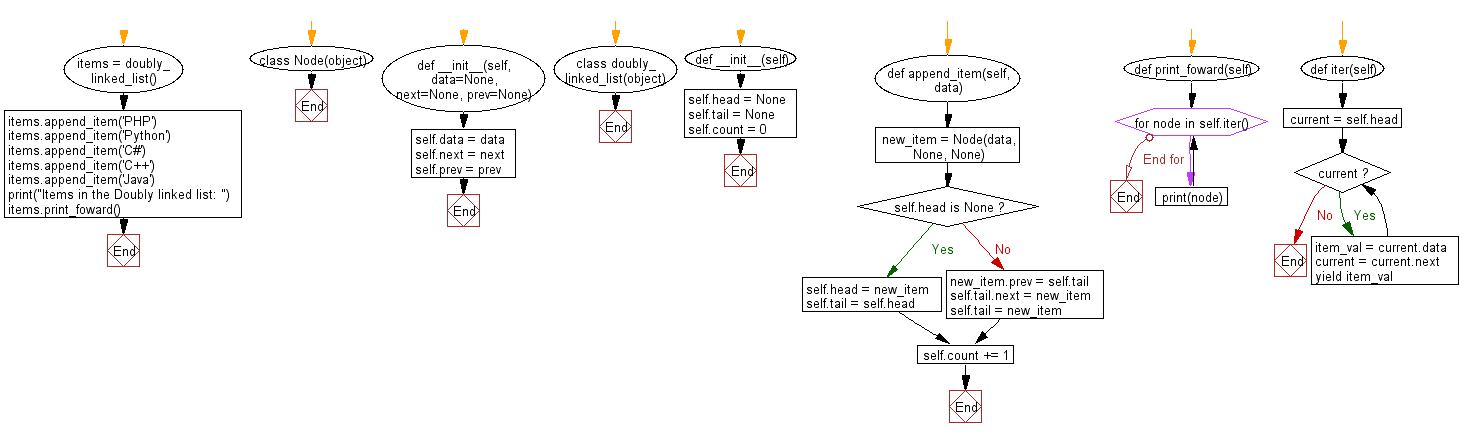
class Node(object):
# Doubly linked node
def __init__(self, data=None, next=None, prev=None):
self.data = data
self.next = next
self.prev = prev
class doubly_linked_list(object):
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.tail = None
self.count = 0
def append_item(self, data):
# Append an item
new_item = Node(data, None, None)
if self.head is None:
self.head = new_item
self.tail = self.head
else:
new_item.prev = self.tail
self.tail.next = new_item
self.tail = new_item
self.count += 1
def print_foward(self):
for node in self.iter():
print(node)
def iter(self):
# Iterate the list
current = self.head
while current:
item_val = current.data
current = current.next
yield item_val
items = doubly_linked_list()
items.append_item('PHP')
items.append_item('Python')
items.append_item('C#')
items.append_item('C++')
items.append_item('Java')
print("Items in the Doubly linked list: ")
items.print_foward()
Sample Output:
Items in the Doubly linked list: PHP Python C# C++ Java
Flowchart:
Python Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
Previous: Write a Python program to delete the last item from a singly linked list.
Next: Write a Python program to create a doubly linked list and print nodes from current position to first node.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Python skills with w3resource's quiz
Python: Tips of the Day
Creates a dictionary with the same keys as the provided dictionary and values generated by running the provided function for each value:
Example:
def tips_map_values(obj, fn):
ret = {}
for key in obj.keys():
ret[key] = fn(obj[key])
return ret
users = {
'Owen': { 'user': 'Owen', 'age': 29 },
'Eddie': { 'user': 'Eddie', 'age': 15 }
}
print(tips_map_values(users, lambda u : u['age'])) # {'Owen': 29, 'Eddie': 15}
Output:
{'Owen': 29, 'Eddie': 15}
- New Content published on w3resource:
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- React - JavaScript Library
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework
