Python: Check if the letters of a given string can be rearranged so that two characters that are adjacent to each other are different
Python heap queue algorithm: Exercise-15 with Solution
Write a Python program to check if the letters of a given string can be rearranged so that two characters that are adjacent to each other are different using Heap queue algorithm.
Note:
If there is no output return the empty string.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
import heapq
from collections import Counter
def reorganizeString(S):
ctr = Counter(S)
heap = [(-value, key) for key, value in ctr.items()]
heapq.heapify(heap)
if (-heap[0][0]) * 2 > len(S) + 1:
return ""
ans = []
while len(heap) >= 2:
nct1, char1 = heapq.heappop(heap)
nct2, char2 = heapq.heappop(heap)
ans.extend([char1, char2])
if nct1 + 1: heapq.heappush(heap, (nct1 + 1, char1))
if nct2 + 1: heapq.heappush(heap, (nct2 + 1, char2))
return "".join(ans) + (heap[0][1] if heap else "")
print(reorganizeString("aab"))
print(reorganizeString("abc"))
print(reorganizeString("aabb"))
print(reorganizeString("abccdd"))
Sample Output:
aba abc abab cdabcd
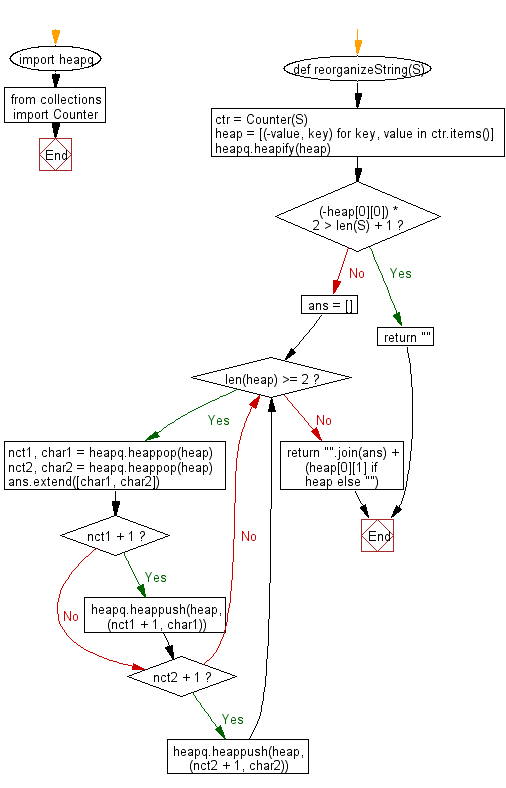
Flowchart:
Visualize Python code execution:
The following tool visualize what the computer is doing step-by-step as it executes the said program:
Python Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
Previous: Write a Python program to get the k most frequent elements from a given non-empty list of words using Heap queue algorithm.
Next: Write a Python program which add integer numbers from the data stream to a heapq and compute the median of all elements.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Python skills with w3resource's quiz
Python: Tips of the Day
Creates a dictionary with the same keys as the provided dictionary and values generated by running the provided function for each value:
Example:
def tips_map_values(obj, fn):
ret = {}
for key in obj.keys():
ret[key] = fn(obj[key])
return ret
users = {
'Owen': { 'user': 'Owen', 'age': 29 },
'Eddie': { 'user': 'Eddie', 'age': 15 }
}
print(tips_map_values(users, lambda u : u['age'])) # {'Owen': 29, 'Eddie': 15}
Output:
{'Owen': 29, 'Eddie': 15}
- New Content published on w3resource:
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- React - JavaScript Library
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework
