Python: Find the nth super ugly number from a given prime list of size k using Heap queue algorithm
Python heap queue algorithm: Exercise-13 with Solution
Write a Python program to find the nth super ugly number from a given prime list of size k using Heap queue algorithm.
Super ugly numbers are positive numbers whose all prime factors are in the given prime list primes of size k. For example, [1, 2, 4, 7, 8, 13, 14, 16, 19, 26, 28, 32] is the sequence of the first 12 super ugly numbers given primes = [2, 7, 13, 19] of size 4.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
import heapq
#Ref.: https://bit.ly/32c9P3A
def nth_Super_Ugly_Number(n, primes):
uglies = [1]
def gen(prime):
for ugly in uglies:
yield ugly * prime
merged = heapq.merge(*map(gen, primes))
while len(uglies) < n:
ugly = next(merged)
if ugly != uglies[-1]:
uglies.append(ugly)
return uglies[-1]
n = 12
primes = [2,7,13,19]
print(nth_Super_Ugly_Number(n, primes))
Sample Output:
32
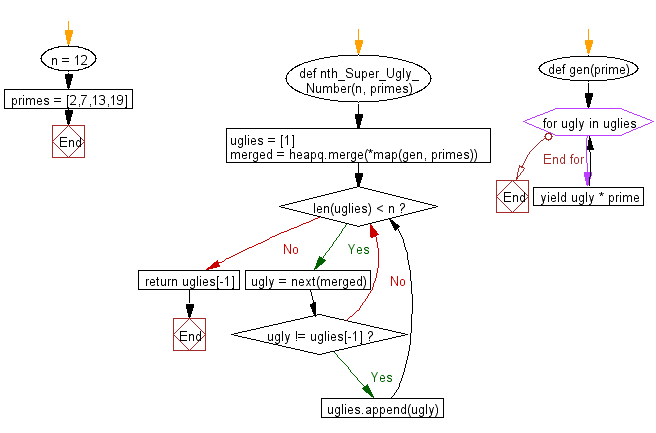
Flowchart:
Visualize Python code execution:
The following tool visualize what the computer is doing step-by-step as it executes the said program:
Python Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
Previous: Given a n x n matrix where each of the rows and columns are sorted in ascending order, write a Python program to find the kth smallest element in the matrix.
Next: Write a Python program to get the k most frequent elements from a given non-empty list of words using Heap queue algorithm.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Python skills with w3resource's quiz
Python: Tips of the Day
Creates a dictionary with the same keys as the provided dictionary and values generated by running the provided function for each value:
Example:
def tips_map_values(obj, fn):
ret = {}
for key in obj.keys():
ret[key] = fn(obj[key])
return ret
users = {
'Owen': { 'user': 'Owen', 'age': 29 },
'Eddie': { 'user': 'Eddie', 'age': 15 }
}
print(tips_map_values(users, lambda u : u['age'])) # {'Owen': 29, 'Eddie': 15}
Output:
{'Owen': 29, 'Eddie': 15}
- New Content published on w3resource:
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- React - JavaScript Library
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework
